The invention of solar panels is a significant milestone in the history of renewable energy. It has revolutionized the way we generate electricity and has opened up a new era in clean energy.
While solar panels have become a household name in recent years, not many people know about their origin or the journey they have gone through to become what they are today. In this blog post, we will take a brief look at the history of solar panels and the various breakthroughs that have led to the development of this technology.
Early experiments
The use of this energy can be traced back to the 7th century BC when the Chinese used magnifying glasses to create fire from the sun’s rays. In the 3rd century BC, the Greeks and Romans used mirrors to light torches for religious ceremonies.
However, it was not until the 19th century that scientists began to experiment with solar energy on a scientific basis. In 1839, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, which later paved the way for the invention of solar cells.
The discovery of the photoelectric effect
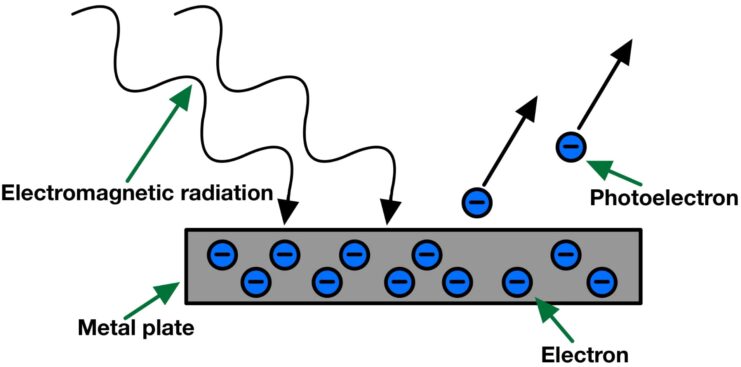
The photovoltaic effect occurs when a material is exposed to light, which causes the release of electrons, generating an electric current. In 1905, Albert Einstein, through his theory of the photoelectric effect, confirmed that light was made up of photons that could knock electrons off atoms. This discovery laid the foundation for the development of solar cells.
The first prototype
In 1954, Bell Labs invented the first practical solar cell. The cell was made of silicon, a semiconductor material that was ideal for converting this energy into electricity. The cell was able to convert sunlight into electricity at an efficiency of 6 percent, which was a significant breakthrough at the time.
Early commercialization
In the 1960s, they were used primarily for space applications. They were used to power satellites and other spacecraft that could not rely on conventional power sources. In 1962, the Telstar satellite, which was powered by them, was launched into orbit. This was the first time that a solar-powered satellite had been launched, and it marked a significant milestone in the commercialization of these cells.
The invention of the first practical solar panel

The first practical solar panel was invented in 1956 by American engineer and inventor, William C. Cherry. The panel was made of a layer of silicon covered with a layer of selenium, and it was able to convert sunlight into electricity at an efficiency of 4 percent. The panel was not as efficient as modern ones, but it was a significant step forward in the development of this technology.
Advancements in the 1960s and 1970s
In the 1960s and 1970s, advancements in this technology led to increased efficiency and lower costs. The development of the first silicon solar cell in 1954 was a crucial breakthrough, but it was not until the 1960s that researchers were able to develop ways to manufacture solar cells in large quantities. In 1973, the University of Delaware developed the first one that could generate enough electricity to power homes.
The Impact of the energy crisis
The energy crisis of the 1970s played a significant role in the development of solar panel technology. The oil embargo of 1973 caused oil prices to skyrocket, leading to a renewed interest in renewable energy sources. Governments and businesses began to invest heavily in research, leading to significant advancements in this technology.
The rise of government support

In the 1980s, governments around the world began to offer incentives for the use of this energy. In the United States, the Solar Energy Research Institute was established in 1977, and in 1978, the Energy Tax Act provided tax credits for homeowners who installed solar energy systems. In Europe, the European Commission launched a research program on renewable energy sources in the 1980s, which included solar energy. These government initiatives helped to further advance solar panel technology and make it more accessible to the public.
The development of thin-film solar panels
In the 1990s, the development of thin-film solar panels brought about a new era in solar technology. They are made by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material onto a substrate such as glass, plastic, or metal. They are much lighter and more flexible than traditional silicon solar panels, making them more versatile and easier to install. They also have a lower production cost, making them more affordable for consumers.
The introduction of photovoltaic technology
Photovoltaic (PV) technology, which is used in modern solar panels, was introduced in the 1980s. PV technology involves the use of semiconducting materials such as silicon to convert solar energy into electricity. This technology has significantly improved their efficiency, making them more cost-effective and reliable.
The increasing efficiency and affordability

Over the past few decades, their efficiency and affordability have continued to improve. Their efficiency has increased from around 6 percent in the 1950s to over 20 percent today. Their cost has also decreased significantly, making them more accessible to homeowners and businesses. In addition, the development of energy storage technologies such as batteries has made it possible to store excess energy for later use.
The future of solar panel technology
It has come a long way since its inception, but there is still much room for improvement. Researchers are currently working on developing more efficient and cost-effective solar panels that can be integrated into buildings and other structures. There is also a growing interest in using solar panels in combination with other renewable energy sources such as wind and hydropower to create a more reliable and sustainable energy grid.
It has the potential to transform the way we generate electricity, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly. It has the potential to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. As more people adopt solar energy, we could see a significant reduction in carbon emissions and a more sustainable energy future.
FAQs
How has the efficiency of solar panels improved over time?
Their efficiency has increased from around 6 percent in the 1950s to over 20 percent today.
What is the average lifespan of a solar panel?
The average lifespan is around 25-30 years.
Can solar panels work on cloudy days?
Yes, they can still generate electricity on cloudy days, although their efficiency may be reduced.
How much do solar panels cost?
Their cost varies depending on factors such as size, efficiency, and location. However, the cost has decreased significantly over the past few decades, making them more affordable for homeowners and businesses.
Is it possible to store excess solar energy?
Yes, it is possible to store excess energy using energy storage technologies such as batteries.
What is the future of solar panel technology?
Researchers are currently working on developing more efficient and cost-effective solar panels that can be integrated into buildings and other structures. This technology has the potential to transform the way we generate and consume energy, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
Solar panel technology has come a long way since its inception in the 19th century. From the discovery of the photovoltaic effect to the development of practical solar cells and panels, solar energy has become a significant source of clean and renewable energy.
Their increasing efficiency and affordability have made them more accessible to consumers, and the development of energy storage technologies has made it possible to store excess solar energy for later use. As we look towards the future, this technology has the potential to transform the way we generate and consume energy, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly.