Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) is a medical intervention designed to prevent HIV infection after potential exposure to the virus. This treatment involves taking antiretroviral drugs for a period of 28 days. The purpose of PEP is to stop the virus from establishing a permanent infection in the body, thereby preventing the onset of HIV disease.
HIV testing is a critical component of the PEP process. It is essential for determining whether the PEP treatment has been successful in preventing infection. Moreover, testing is crucial for early detection of the virus, which can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
The timing of testing in relation to PEP is a complex issue that requires careful consideration. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on when to test for HIV during and after the completion of PEP, offering valuable insights based on current research and medical guidelines.
Understanding PEP and HIV Risk
PEP is a short-term antiretroviral treatment that is typically started within 72 hours after a potential exposure to HIV. The treatment lasts for 28 days and is designed to prevent the virus from replicating and establishing a permanent infection in the body. It’s important to note that PEP is not a cure for, but a preventive measure that can significantly reduce the risk of infection if taken correctly and started promptly after exposure.
The risk of transmission varies depending on several factors, including the type of exposure, the status of the source person, and the presence of other sexually transmitted infections. PEP can significantly reduce this risk, but it’s not 100% effective. Therefore,test remains crucial for anyone who has been potentially exposed to the virus, regardless of whether they have taken PEP or not.
Understanding the role of PEP in reducing HIV risk is essential for making informed decisions about testing. While PEP can significantly lower the risk of infection, it does not eliminate it completely. Therefore, testing is necessary to confirm whether the PEP treatment has been successful in preventing HIV infection.
During PEP
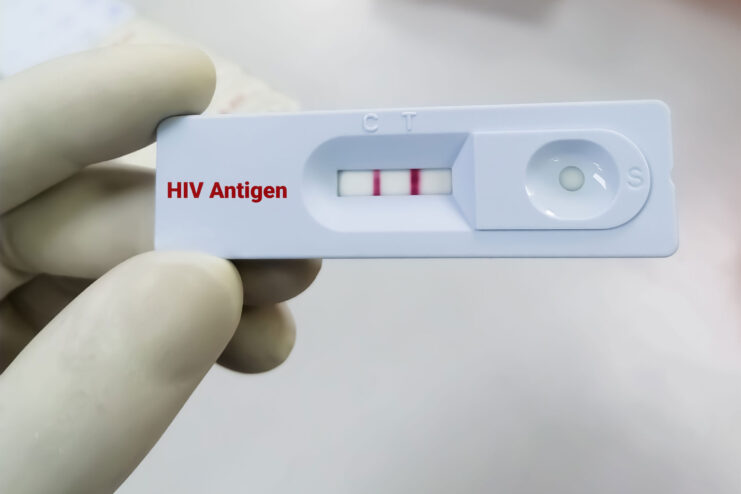
Testing for HIV during the PEP treatment period is a crucial step in managing potential exposure to the virus. Early detection of HIV can lead to better health outcomes and can prevent further transmission of the virus.
However, it’s important to understand the concept of the “window period” in HIV testing. The window period refers to the time between potential exposure to the virus and the point when a test can reliably detect the infection.
During PEP can be challenging due to the window period. Most tests detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the virus. However, these antibodies may not be detectable until several weeks after exposure. Therefore, an HIV test taken too soon after exposure may not provide accurate results.
When to get tested during PEP depends on several factors, including the type of exposure and the specific circumstances of the individual. Generally, an initial test is recommended at the start of PEP to establish a baseline status. Further testing may be advised based on the healthcare provider’s assessment and the individual’s specific situation.
Testing after Completion of PEP
Testing for HIV after the completion of PEP is critical to confirm the individual’s status. This post-PEP tes is necessary because the body may take time to produce enough antibodies for the HIV test to detect, especially if PEP has delayed seroconversion, the process by which a person develops detectable antibodies to HIV.
The window period for HIV testing after completing PEP is a crucial consideration. Most guidelines recommend an test at the end of the PEP treatment and anothertest four to six weeks after completing PEP. However, the exact timing may vary depending on the type of test used and the specific circumstances of the individual.
The guidelines for post-PEP test are designed to ensure that any infection is detected as soon as possible. It’s important to adhere to these guidelines and to consult with a healthcare provider about any concerns or questions regarding testing after PEP.
Factors Affecting HIV Testing Accuracy

Several factors can affect the accuracy of test results during and after PEP. One of the main factors is the window period, which can delay the detection of HIV antibodies. Other factors include the type of test used, the individual’s immune response, and the potential presence of other sexually transmitted infections.
Follow-up testing is a crucial aspect of HIV testing during and after PEP. Because of the window period and other potential factors, a single test may not be sufficient to confirm an individual’s status. Follow-up test can help ensure that any infection is detected and treated as soon as possible.
Adherence to test guidelines is essential for accurate testing. It’s important to understand that while PEP can significantly reduce the risk of HIV infection, it does not guarantee that an individual will remain HIV-negative. Therefore, regular test is necessary for anyone who has been potentially exposed to the virus, regardless of whether they have taken PEP or not.
Communicating with Healthcare Providers
Communication with healthcare providers is a key aspect of the PEP and testing process. Healthcare providers can provide valuable guidance and support, helping individuals understand their specific PEP regimen and testing schedule.
Effective communication with healthcare providers involves asking questions and expressing any concerns or uncertainties about HIV testing. It’s important to be open and honest about any potential exposure to and to provide accurate information about any symptoms or health issues.
Healthcare providers can also provide resources and referrals for additional support, such as counseling services and support groups. These resources can be invaluable for individuals undergoing PEP and HIV test, providing emotional support and helping them navigate the challenges of this process.
Addressing Psychological Impact

Undergoing PEP and testing can have a significant psychological impact. The fear of a potential infection and the anxiety associated with waiting for test results can be stressful and emotionally challenging.
It’s important to acknowledge these feelings and to seek support when needed. This can involve talking to a trusted friend or family member, consulting with a mental health professional, or joining a support group for individuals who have undergone PEP or are living with HIV.
Coping strategies can vary from person to person, but some general tips include practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and focusing on positive coping mechanisms, such as engaging in enjoyable activities and maintaining social connections.
Testing Options and Availability
There are several options for HIV testing, including rapid tests, lab-based tests, and self-testing kits. Rapid tests provide results within minutes, while lab-based tests may take longer but can be more accurate. Self-test kits allow individuals to test for at home, providing a convenient and private option for those who prefer not to go to a healthcare clinic.
HIV testing services are widely available through healthcare clinics, community organizations, and online resources. Many of these services offer free or low-cost testing, and some also provide counseling and support services for individuals undergoing testing.
It’s important to choose a testing option that is suitable for the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Regardless of the test option chosen, it’s crucial to follow the instructions carefully and to consult with a healthcare provider if there are any concerns or questions about the test process.
Supportive Resources and Counselling

Supportive resources and counseling services can play avital role in the PEP and testing process. These resources can provide emotional support, practical advice, and valuable information, helping individuals navigate the challenges of potential exposure and test.
Counseling services can provide a safe and confidential space for individuals to discuss their fears and concerns about testing. These services can also provide guidance on coping strategies and can offer referrals to other support services, such as support groups and mental health professionals.
Support groups can provide a sense of community and shared understanding, helping individuals feel less alone in their experiences. These groups can offer emotional support, practical advice, and a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
Importance of Regular HIV Testing
Regular HIV testing is crucial for anyone who is sexually active, particularly those who have multiple partners or who do not consistently use condoms. Regular testing allows for early detection of HIV, which can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
Beyond the PEP period, regular HIV test is a key component of sexual health. It’s important to understand that while PEP can significantly reduce the risk of HIV infection following potential exposure, it does not protect against future exposures. Therefore, regular test remains crucial for anyone who is at risk of infection.
Educating individuals about the importance of regular testing and other risk factors for infection is a key aspect of prevention. This includes promoting safer sex practices, such as using condoms consistently and correctly, and providing information about other preventive measures, such as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
Conclusion
HIV testing during and after PEP is a complex issue that requires careful consideration and adherence to medical guidelines. It’s crucial for anyone who has been potentially exposed to to understand the importance of testing and to follow the recommended testing schedule.
The significance of testing extends beyond the PEP period. Regular test is a key component of sexual health and prevention, allowing for early detection of the virus and reducing the risk of transmission.
Navigating the PEP and HIV testing process can be challenging, but there are numerous resources and support services available to help. By seeking support, communicating effectively with healthcare providers, and adhering to test guidelines, individuals can ensure that they are taking the necessary steps to protect their health and the health of others.
Related Posts:
- HIV ELISA Test And HIV ECLIA Test: The Power of Accuracy
- The Causes of Vaginal Bleeding After Sex (Post…
- Contraception After Delivery: A Comprehensive Guide
- HIV RNA / DNA PCR Test – Nucleic Acid Amplification…
- HIV CMIA Test Accuracy: What You Need to Know
- False Negative HIV ELISA Test: Decoding the Mystery












