Throat Gonorrhea, colloquially known as “The Clap,” is an infection that affects the throat, caused by the bacteria Neisseria Gonorrhea. While it might sound unfamiliar to many, it’s essential to understand this condition, its symptoms, and preventive measures.
What Exactly is Throat Gonorrhea?
Throat Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that specifically targets the throat. It’s a manifestation of the gonorrhea bacteria, which can also affect other parts of the body, such as the urethra, anus, and genitals.
Spotting the Symptoms:
In most cases, Throat Gonorrhea is a silent invader. About 90% of infected individuals don’t show any symptoms, making it a stealthy condition. However, for the remaining 10%, symptoms might include:
- A persistent sore throat
- Fever
- Swollen neck glands These symptoms typically manifest between 2 to 10 days post-exposure.
Transmission: How Do You Get It?

The primary mode of transmission for Throat Gonorrhea is through unprotected oral sex with an infected partner. The risk is significantly higher when engaging in receptive penile oral sex compared to receptive vaginal oral sex. This means you’re more likely to contract it when performing oral sex on a male partner with gonorrhea than on a female partner.
The Risk of Spreading:
If you’re infected, it’s crucial to understand that you can transmit Throat Gonorrhea to your partner during unprotected oral encounters. If your partner starts showing symptoms like painful urination or unusual discharge, it’s a sign that you should get tested.
Diagnosis: The Path to Confirmation
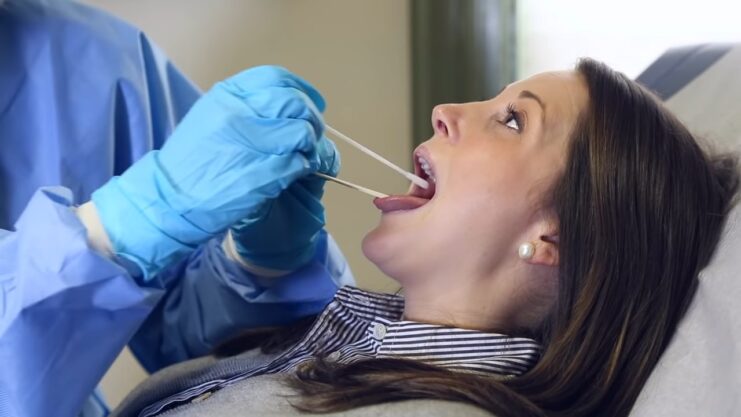
If you suspect you might have Throat Gonorrhea, it’s essential to see a doctor promptly. The doctor will take a specialized swab from your throat, which will then be sent to a lab for testing. Remember, a regular strep throat swab won’t detect this condition, so always specify your concerns to your healthcare provider.
Treatment Options:

The most common treatment for Throat Gonorrhea is an antibiotic injection, specifically Ceftriaxone. For those who can’t take the injection, oral medications are available. It’s crucial to follow up with your doctor to ensure the infection is entirely eradicated.
Prevention is Better than Cure:
The best way to protect yourself from Throat Gonorrhea is by using a condom during oral sex. Safe practices can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Associated Risks:

Throat Gonorrhea doesn’t come alone. If you’re diagnosed with it, there’s a chance you might have gonorrhea in other parts of your body. Moreover, it’s often associated with other STDs like HIV, Syphilis, and Hepatitis B. Regular screenings and check-ups are advisable.
Conclusion:
Throat Gonorrhea, while less talked about, is a significant concern. Awareness, safe practices, and regular check-ups are the keys to ensuring you and your partner’s health. Always prioritize your well-being and seek medical advice when in doubt.