Oral thrush, also known as oropharyngeal candidiasis, is a condition that arises due to a fungal infection in the mouth and tongue. This infection is primarily caused by a group of yeast organisms known as Candida. It’s important to note that the presence of a small amount of these fungal organisms in your mouth and gastrointestinal tract is perfectly normal and usually doesn’t cause any harm. However, when these organisms start to multiply uncontrollably, it can lead to an infection, which is what we commonly refer to as oral thrush.
Oral thrush is generally a mild infection and can be easily treated with antifungal medications. However, it can also serve as a warning sign of a weakened immune system. This is often seen in individuals with poorly-controlled diabetes, cancer, and untreated HIV/AIDS infection.
Symptoms of Oral Thrush: What to Look Out For
The symptoms of oral thrush can vary from person to person, but there are a few common signs that you can look out for. These include:
- Whitish or reddish patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, tonsils, and gums
- A pain or burning sensation around the tongue and mouth
- Altered taste or loss of taste over the tongue
- Painful cracks at the corners of the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing (in cases of esophageal candidiasis)
One of the distinguishing features of oral thrush is that the white coating can be scraped off, revealing reddish, raw patches underneath. These patches can sometimes bleed slightly. This characteristic helps differentiate oral thrush from other lesions such as lichen planus or oral hairy leukoplakia, where the lesions cannot be wiped away.
While oral thrush is usually diagnosed clinically through its appearance and history, additional tests such as a fungal smear or biopsy may sometimes be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other similar-looking conditions.
Is It Contagious?
Oral candidiasis is classified as an opportunistic infection. This means that a normally harmless organism takes advantage of a weakened immune system and causes an invasive infection. It’s important to note that oral thrush is not considered contagious. It cannot be transmitted through kissing or sharing food and utensils.
Risk Factors
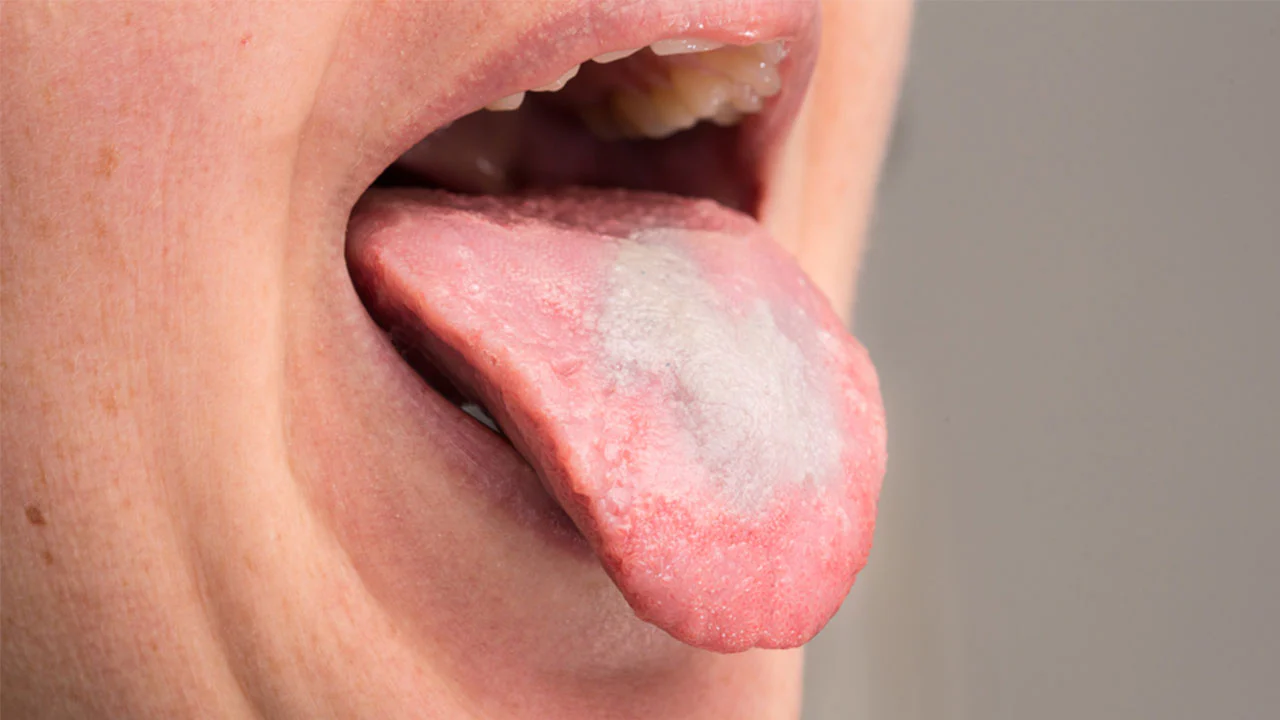
Certain conditions can increase an individual’s susceptibility to oral thrush. These include:
- Prolonged or high dose antibiotic use
- Prolonged or high dose corticosteroid use, including steroid-based inhalers for asthma
- Cancers such as leukemia, or undergoing treatment such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- HIV infection / AIDS
- Poorly-controlled diabetes
- Ill-fitting dentures and poor dental hygiene
- Cigarette smoking
Treatment and Prevention
Oral thrush can usually be treated with a short course of antifungal medications. However, it’s also crucial to investigate and manage any underlying conditions that may have contributed to the development of the infection.
Complicated infections are rare unless the individual is immuno-compromised. In such cases, the infection can enter the bloodstream and spread to other organs such as the brain, heart, and liver.
If you suspect that you may have oral thrush or any related conditions, it’s best to consult a doctor early for a proper assessment. If you are in or around Singapore, please make an appointment with any of our clinics to have a complete evaluation by our specially-trained medical professionals.
FAQ
Can oral thrush cause complications if left untreated?
Yes, if left untreated, oral thrush can lead to more serious systemic infections, especially in people with weakened immune systems. The Candida fungus can spread to other parts of the body, including the lungs, liver, and skin.
Can babies get oral thrush?
Yes, oral thrush is quite common in infants and newborns. It can cause white patches in the baby’s mouth and on the tongue. In most cases, it’s harmless and clears up with treatment, but if your baby has oral thrush, it’s best to see a doctor.
Can it be a sign of other health problems?
Yes, oral thrush can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health problem that has weakened the immune system, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer.
Can oral thrush be cured completely?
Yes, with proper treatment, oral thrush can be completely cured. However, it can recur if the underlying cause is not addressed.
Final Words
Oral thrush is a common condition that can cause discomfort and pain, but it is usually easily treatable. However, it can also be a sign of a weakened immune system, so it’s important not to ignore the symptoms.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is key to preventing oral thrush and other oral health problems. This includes regular brushing and flossing, using a good quality mouthwash, and regular dental check-ups.
If you wear dentures, ensure they fit properly and are cleaned regularly to prevent the growth of Candida. If you have a medical condition such as diabetes or HIV, it’s important to manage your condition effectively to prevent complications like oral thrush.
Remember, your mouth is a window to your overall health. So, take care of it, and it will take care of you. If you suspect you may have oral thrush or any related conditions, don’t hesitate to seek medical help. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Related Posts:
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- STD Symptoms in Receptive Oral Sex: The Hidden Threat
- Micropenis: Causes, Treatment, and Coping Strategies
- Gonorrhea - From Symptoms to Treatment
- Getting HIV From Oral Sex: What's the Real Risk?
- Vaginal Infection: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention












