Gout and hyperuricaemia are conditions that have been known to mankind for centuries. Often misunderstood and misdiagnosed, they can cause significant pain and discomfort. In this article, we’ll delve deep into these conditions, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and the steps you can take to manage them effectively.
Gout and hyperuricaemia are closely related, but they are not the same. Understanding the distinction between them is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
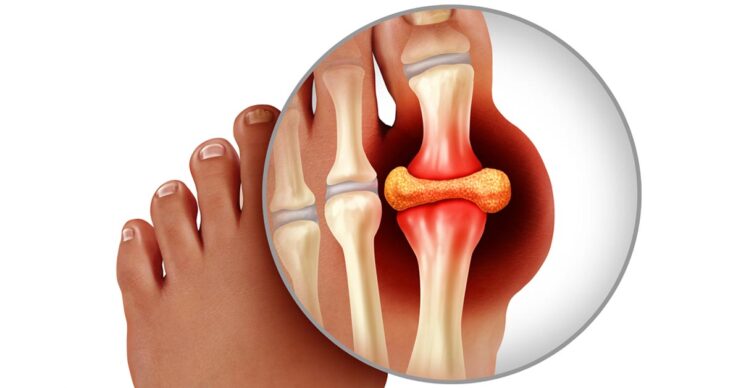
Gout is a type of arthritis that results from an excess of uric acid in the joints. This surplus acid leads to the formation of sharp, needle-like crystals in a joint, causing intense pain, redness, and swelling.
Hyperuricaemia, on the other hand, refers to an elevated level of uric acid in the blood. While it increases the risk of developing gout, not everyone with hyperuricaemia will experience gout attacks.
Who is at Risk?
Gout can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk. Consuming foods high in purines, being overweight, and certain medical conditions can predispose individuals to gout. Men are more frequently affected than women, and some medications can also trigger gout.
Recognizing a Gout Attack
A gout attack can be an excruciating experience. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is the first step towards seeking timely treatment.
The Onset and Symptoms
Gout attacks often strike without warning, typically starting at night. The most common site is the big toe, but other joints can also be affected. The affected joint becomes red, swollen, and extremely tender, with even the slightest touch causing immense pain.
Immediate Actions to Take
If you suspect a gout attack, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early treatment can alleviate pain and prevent complications. Resting the affected joint, applying hot or cold compresses, and avoiding putting weight or pressure on it can provide some relief.
The Long-Term Implications of Ignoring Gout
Ignoring gout can have severe consequences. Continuous attacks can lead to joint damage and other complications.
The Dangers of Untreated Gout
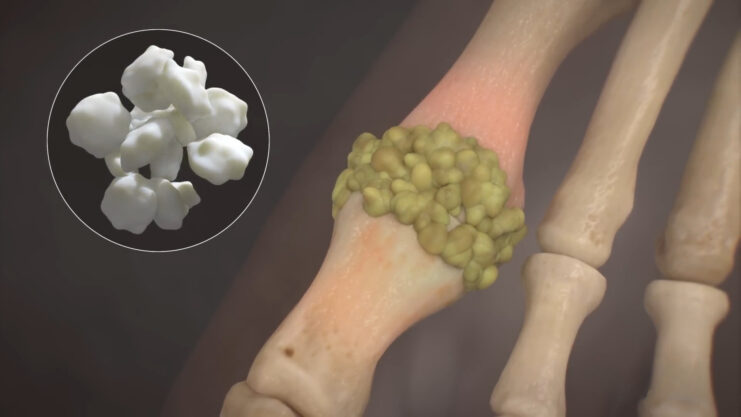
Without treatment, gout attacks can persist for days or even weeks. Over time, repeated attacks can affect multiple joints and last longer. Chronic untreated gout can lead to the formation of tophi-lumps of uric acid crystals. These can be seen on the elbows, fingers, and toes. Additionally, there’s a risk of developing kidney stones or even kidney disease.
Preventative Measures

To prevent future attacks, doctors can prescribe medications that help reduce uric acid levels or prevent its formation. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and avoiding alcohol, can also help. Staying hydrated and following a low-purine diet can significantly reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Foods to Avoid Completely:
- Organ meats like liver, kidney, and brain.
- Red meats like beef and mutton.
- Certain fish like sardines.
- Some fruits like strawberries and durians.
- Alcohol, especially beer and sweet wines.
- Bean products including tofu and soy milk.
- Foods to Consume in Moderation:
- Vegetables like asparagus and spinach.
- Certain fish like tuna and salmon.
- Processed meats like ham and sausages.
- Whole grains and certain seafood.
- Foods Generally Safe to Consume:
- Skimmed milk and egg whites.
- Most vegetables and fruits.
- Bread, noodles, and pasta.
- White meats like chicken and fish.
Dietary Interventions for Gout Management
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing gout and hyperuricaemia. By understanding which foods to embrace and which to avoid, one can significantly reduce the risk of gout attacks and improve overall health.
The Low-Purine Diet
A low-purine diet is often recommended for those with gout or hyperuricaemia. Purines are natural substances found in many foods, and when broken down in the body, they produce uric acid. By limiting purine intake, one can effectively reduce uric acid levels.
- Benefits of a Low-Purine Diet:
- Reduces the risk of gout attacks.
- Helps in managing hyperuricaemia.
- Supports overall joint health.
Foods to Embrace
While many foods are restricted on a low-purine diet, there are plenty of delicious and nutritious options to include:
- Heart-Healthy Choices:
- Olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables, especially cherries, which have been shown to reduce uric acid levels.
Lifestyle Changes for Gout Prevention
Beyond dietary interventions, several lifestyle changes can help in preventing gout attacks and promoting overall well-being.
Importance of Hydration

Drinking ample water daily helps flush out excess uric acid from the body, reducing the risk of crystal formation in the joints.
- Hydration Tips:
- Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Limit sugary and caffeinated beverages.
- Herbal teas can be a good addition, especially those with anti-inflammatory properties.
Weight Management and Exercise
Being overweight increases the risk of gout. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce this risk.
- Exercise Benefits:
- Strengthens joints and muscles.
- Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness.
- Boosts overall mood and well-being.
Medications and Treatment Options
While lifestyle and dietary changes are crucial, medications play an essential role in managing gout and hyperuricaemia.
Commonly Prescribed Medications
Several drugs can help reduce uric acid levels, prevent gout attacks, or treat symptoms during an attack:
- Uric Acid Lowering Drugs: Such as allopurinol and febuxostat.
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen.
- Colchicine: Specifically used to treat gout attacks.
The Role of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital for those with gout or hyperuricaemia. Monitoring uric acid levels, assessing joint health, and adjusting medications as needed can ensure optimal management of the condition.
FAQ
Are there any natural remedies for gout relief?
Yes, some natural remedies like apple cider vinegar, ginger, and turmeric have anti-inflammatory properties that can provide relief during a gout attack. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies.
Can women get gout?
While men are more commonly affected, women can also develop gout, especially after menopause when uric acid levels tend to rise.
Is gout genetic?
There is a genetic component to gout. If other family members have had gout, your risk might be higher. However, lifestyle and dietary factors play a significant role as well.
Can stress trigger a gout attack?
Stress can be a contributing factor. While it doesn’t directly cause gout, it can be a trigger for some people, especially when combined with other risk factors.
Are there any specific beverages to avoid?
Alcohol, especially beer, can increase uric acid levels. Sugary drinks and those with high fructose content can also contribute to gout risk.
Final Words
Gout and hyperuricaemia, though complex, are conditions that can be managed effectively with the right knowledge and approach. By understanding the intricacies of these conditions and making informed choices, one can lead a life of comfort and well-being. Always remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.