The world of internet connectivity can often feel overwhelming, full of technical jargon and specifications that seem nearly impossible for the layperson to understand. One such topic revolves around the cables that help deliver internet services to our homes and offices: the coaxial cable.
So, you may ask, “Can I use any coaxial cable for the internet?” The quick answer is, “Not exactly.” For a more detailed explanation, stick around as we dive into the complexities of coaxial cables, their different types, uses, and how they impact your internet speed and stability.
A Brief Overview
Before discussing the suitability of any coaxial cable for internet usage, it’s important to understand what it actually is. Coaxial cables are a type of transmission line, designed to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. These cables are constructed with a core conductor, an insulating layer, an outer conductor (usually a metal shield), and an insulating outer layer or jacket.
The name “coaxial” refers to the common axis of these layers. This construction allows coaxial cables to deliver a stable signal and guard against interference, making them ideal for a variety of applications, including television signals, telephone trunk lines, and yes, internet connectivity.
Different Types of Coaxial Cables
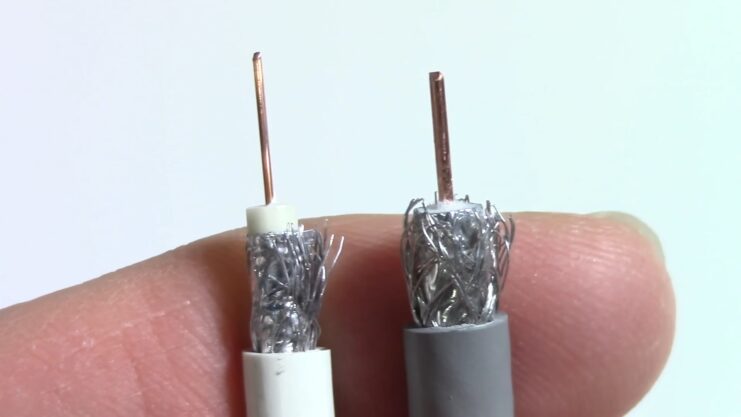
Although they may look similar on the surface, not all coaxial cables are created equal. They differ in their construction, impedance, loss characteristics, and even size. The two most common types used for home internet and TV are RG6 and RG59.
RG6
RG6 is currently the standard for home internet and TV connections. The “RG” stands for “Radio Guide,” a term dating back to the World War II era. The “6” is just a number assigned by the U.S. military to classify the cable.
RG6 cables are specifically designed for high-frequency and high-bandwidth applications. They have larger conductors, which means they can carry more data. They also have a thicker dielectric insulator, which means less signal loss over distance.
RG59
RG59 cables are another type of coaxial cable, but they are generally considered outdated for most modern internet and TV applications. These cables were designed for lower-frequency and lower-bandwidth applications. They tend to have higher signal loss over distance, meaning that they’re not ideal for delivering high-speed internet.
So, Can I Use Any Coaxial Cable For The Internet?

Considering the differences in construction and performance between RG6 and RG59, you might have already guessed that using just any coaxial cable may not be the best idea for your internet connection.
Here’s why:
Signal Loss and Internet Speed
Signal loss (also known as attenuation) is a crucial factor affecting your internet speed. RG59, being designed for lower frequencies, has a higher signal loss compared to RG6. This means if you use RG59 for your internet, you may experience slower speeds, especially over longer distances.
Frequency Range and Bandwidth
RG6 supports a wider frequency range and higher bandwidth compared to RG59. This means RG6 is capable of delivering more data—critical for high-speed internet services.
Interference
Coaxial cables are designed to resist interference, but RG6 cables generally do a better job compared to RG59. This is mainly because RG6 cables have a thicker and denser shield. Interference can cause data loss and slower internet speeds, so a cable that better resists interference (like RG6) will provide a more reliable internet connection.
The Verdict
While you technically could use any coaxial cable to set up your internet, not every cable will give you the best performance. The differences between RG6 and RG59 may not seem huge, but they can have a significant impact on your internet speed and reliability.
Generally, for home internet services, RG6 is the recommended choice. Its wider frequency range, lower signal loss, and better interference protection make it more suitable for high-speed internet. But if you’re in a pinch, and all you have is an RG59 cable, you can use it—it just might not deliver the high-speed connection you’re expecting.
However, there’s another aspect that we need to discuss when it comes to coaxial cables: the connectors.
The Role of Connectors
Coaxial cable connectors are also a vital part of the equation, and choosing the right one can impact your internet connectivity. The most common types of connectors for home internet services are F-type connectors, but even within this category, there are differences.
The two main types of F-type connectors are screw-on and compression. Screw-on connectors are easier to install, but they tend to have higher signal loss compared to compression connectors. Compression connectors, on the other hand, provide a tighter, more secure connection, resulting in better signal quality.
When setting up your internet, ensure that the connectors are well-fitted, as loose connections can lead to signal loss and affect your internet speed.
Upgrading Your Coaxial Cables
If you find that your internet speed is slower than expected, and you’re using an RG59 coaxial cable, it might be time to consider upgrading to an RG6 cable. The process is relatively straightforward, but if you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, you may want to hire a professional.
Before replacing your cable, here’s what you should do:
- Measure the length of the cable you need. It’s better to have a little extra length to account for any unexpected issues.
- Purchase an RG6 coaxial cable of the required length. You can find these at any electronics store or online.
- Ensure you have the right connectors. Most RG6 cables come with F-type connectors, but it’s always good to double-check.
- Once you have your cable, replace the old one by disconnecting the RG59 cable and replacing it with the RG6. Make sure all connections are secure.
You should notice an improvement in your internet speed and connectivity after replacing your cable. However, if you’re still having issues, it might be worth talking to your internet service provider. There could be other issues affecting your connection, such as problems with the modem or the service itself.
Exploring Beyond RG59 and RG6
While RG59 and RG6 are the most common types of coaxial cables for residential internet, there are other types out there used in various scenarios. For instance, RG11, a thicker and more robust cable, is used for longer distances where signal loss might be a concern.
RG11 Coaxial Cables

RG11 cables have an even larger conductor and a thicker dielectric insulator than RG6. This design reduces signal loss over greater distances, making it suitable for runs exceeding 200 feet.
However, RG11 is not typically used in residential settings due to its size and cost. Its larger diameter makes it harder to bend and maneuver, particularly in tight spaces. Nevertheless, it’s a good option for certain applications, such as community antenna television (CATV) or in situations where the cable has to traverse long distances without signal boosters.
Coaxial Cables and Ethernet
Coaxial cables aren’t the only choice for internet connectivity; Ethernet cables are another common choice. Ethernet cables, like Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7, are widely used for wired internet connections and might be a suitable alternative depending on your internet needs.
Ethernet cables typically offer faster speeds than coaxial cables and have lower latency, making them ideal for activities that require real-time response, like gaming or video conferencing. However, they’re more susceptible to interference and aren’t as well-suited for long distances as coaxial cables.
The Future of Coaxial Cables

With fiber-optic technology becoming more widespread, you might be wondering what place coaxial cables have in the future of internet connectivity. While it’s true that fiber-optic cables offer faster speeds and lower latency, coaxial cables still have a significant role to play.
Many existing telecommunications infrastructures rely heavily on coaxial cables. Upgrading these networks to fiber-optic is costly and time-consuming. Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks, which combine the speed of fiber-optic with the robustness and widespread availability of coaxial cables, are a common solution. These networks use fiber-optic cables for long-distance transmission, then switch to coaxial cables for the “last mile” to individual homes and businesses.
Wrapping Up
Internet connectivity is a complex field, and while it may seem as simple as connecting a cable, the type of cable you use can significantly impact your experience. Coaxial cables, specifically RG6 cables, are designed for high-speed internet connections. So, while you technically could use any coaxial cable for the internet, if you want a fast, reliable connection, choosing the right cable is crucial.
Whether you’re setting up a new connection or troubleshooting an existing one, understanding the role of coaxial cables can help you ensure you’re getting the best possible internet speed and reliability.
Related Posts:
- Asymmetric Vulva? Not a Problem: Breaking Down the Stigma
- Smart TV Internet Hacks: 5 Tips for Enhancing Speed…
- Why You Shouldn’t Use Yoni Pearls - Discover the…
- 12 Best Modern VHS Player 2024 - For Every Type Of Use
- 10 Ways to Use Gaming to Earn Some Money on the Side in 2024
- Understanding Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: The Itch You…












