Skin surgery is commonly done either for diagnosis or removal of a skin lesion. It is done under local anaesthesia, meaning procedure is mostly painless. These include skin biopsy, electrosurgery, excision and cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen).
Different Types
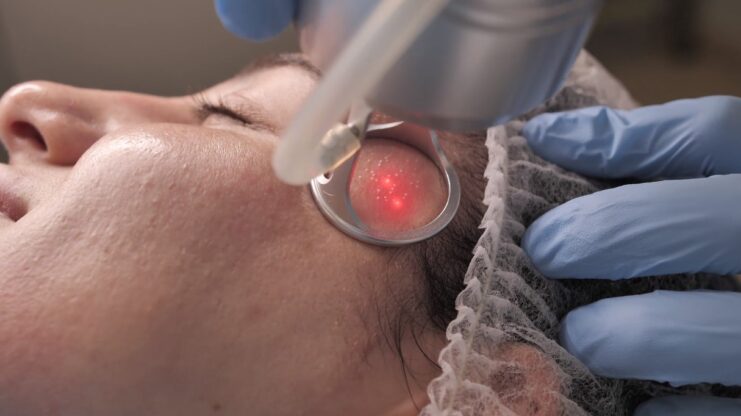
1) Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy is an easy and quick procedure done to remove a piece of skin. It is then sent to the laboratory for further identification under microscope so a diagnosis can be made.
Why do I need a skin biopsy?
Skin biopsy is usually done for diagnosis of your skin condition. A lot of times, skin conditions can mimic one another. For example, a skin cancer (melanoma) can sometimes look similar to a harmless mole. Skin biopsy provides additional vital information when a definite clinical diagnosis cannot be confirmed. It can even tell us what kind of skin cancer it is so the appropriate treatment can be advised.
All skin biopsy is done under local anesthesia. A small injection is given so the skin quickly becomes numb and the procedure is painless.
There are different types of skin biopsy depending on the type and the location of the skin condition.
Punch biopsy
The punch biopsy blade takes a small round core of tissue ranging from 3-4 mm in diameter. It is a quick procedure. A stitch may be required or, if the wound is tiny (most of the time), it will heal adequately without a stitch.
Shave biopsy
A shave biopsy is done with a scalpel or razor blade and may be used if the skin lesion is suspected to only affect the top layers of the skin. A very superficial slice of the skin is removed. No stitches are required usually. There will be a small scab that will normally take 1-2 weeks to heal.
Incisional biopsy
Sometimes when a larger piece of skin is needed to make a correct diagnosis, a deeper biopsy is done. For incisional biopsy, stitches are usually required after the removal.
2) Electrosurgery
Electrosurgery uses high frequency electric current that generates heat to either stop bleeding or to remove or destroy the abnormal skin lesion. This is an extremely effective method for removal of multiple benign skin lesions such as harmless moles, warts, molluscum contagiosum, cherry angioma, skin tags and even solar lentigines (sun spots). This procedure gives a very good cosmetic effect. Healing usually takes about 3-4 weeks.
However, this method may not be used for skin conditions that require confirmatory diagnosis such as suspected skin cancer or suspicious looking moles. In such cases, biopsy or excision is necessary.
3) Excision
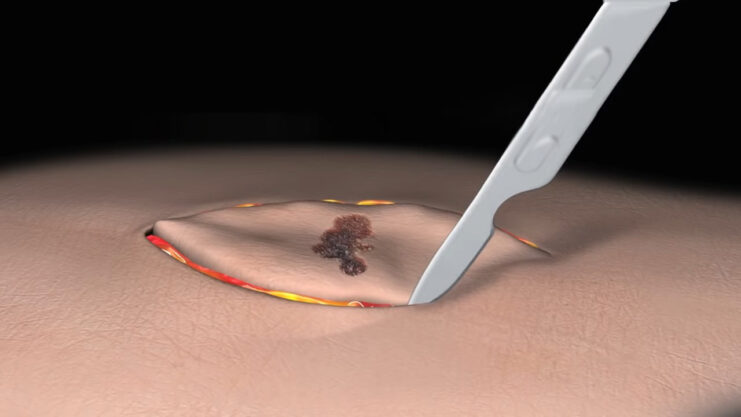
In excision, skin lesion is removed completely under local anaesthesia. It is usually done if the skin lesion is highly suspicious of skin cancer. This is because skin cancer usually penetrates deeper into the skin tissue although they may be visibly small. If not removed completely, it may be dangerous to you. It usually requires stitches, and may leave a small scar after the wound heals completely.
Sounds scary, is excision necessary? Excision is necessary for skin lesions highly suspicious of skin cancer because skin cancer like melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma is known to be very dangerous.
4) Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a technique using liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy skin lesions. Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold. It will freeze any living tissue it comes into contact with. It can be used to treat skin conditions like warts, skin tags, and small lumps and bumps on the skin. Sometimes, a few treatment sessions may be required for larger or thicker skin lesions like warts.
Cryotherapy can be a little uncomfortable but is usually not painful. Most people find it quite bearable.
If you have any lesions on your skin that you are concerned about, you should consult a doctor immediately to get it properly assessed. A minor skin biopsy/surgery may be required and it is not scary at all!
FAQs
How long does it take for the skin to heal after these procedures?
The healing time varies depending on the procedure. For instance, after a shave biopsy, the skin usually heals within 1-2 weeks. After excision, it might take a bit longer, especially if stitches are involved. Always follow post-procedure care instructions to ensure optimal healing.
Are there any side effects to these procedures?
Some common side effects include temporary redness, swelling, and discomfort at the procedure site. There’s also a risk of infection, scarring, or an allergic reaction to the anesthesia, though these are rare.
How can I minimize scarring after a procedure?
Keeping the area clean, moisturized, and protected from the sun can help minimize scarring. Your doctor might also recommend scar-minimizing creams or ointments.
Can these procedures be done on any part of the body?
Yes, these procedures can be performed on most parts of the body. However, the approach might vary depending on the location and the type of skin lesion.
How often should I check my skin for suspicious lesions?
It’s a good practice to do a self-examination once a month. If you notice any changes or new lesions, consult a doctor. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist are also recommended.
Are these procedures covered by insurance?
Coverage varies depending on the insurance provider and the reason for the procedure. It’s best to check with your insurance company beforehand.
Final Words
Our skin, being the largest organ, is often exposed to various environmental factors and is susceptible to various conditions. While many skin lesions are benign, it’s crucial to be proactive in monitoring any changes and seeking medical advice when in doubt.
Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference, especially when dealing with conditions like skin cancer. Remember, when it comes to your health, it’s always better to be safe and informed.
Related Posts:
- Skin Cancers: From Sunburn to Skin Health
- Vaginal Lumps and Bumps: What Every Woman Should Know
- Curved Monitor: Pros And Cons - Should You Get It Or Not?
- What Does Sperm Cramps Mean in Men? Should You Be…
- Hematospermia (Blood in the semen) Should You Be Worried?
- 10 Ways to Get Rid of Skin Pigmentation: Nature's Best












